If you are looking for any blog in particular, please click on the labels to the right here to find what you are looking for.
Hi there!
My name is Tom and this is my Blog space, where I will be posting my learning about digital ways of teaching for my future students. I am a second year Pre-service Teacher, studying to teach ITD and HPE. I have limited experience using web spaces but am eager to learn and try new things.
Myself as a contemporary teacher
My initial reactions towards beginning this unit on digital pedagogies came from feelings of self-doubt and lack of confidence. This was due to my inexperience with digital platforms. I have never been in a situation where I needed to create a website for an online blog or any other tools.
Elaborate on your emotions on engaging further with this unit? Positive, negative. Indifferent?
I began to feel intrigued and curious as I will know I will need these tools when teaching high school students who frequently use social media and many other online platforms.
To what extent do you have the commitment to actively interrogate your emotions, and your beliefs about creative pedagogy (that extends beyond the mere delivery of information to your learners)? How might you be challenged to engage as you enter this unit?
Personally, as a 21st century learner myself, I am committed to upskilling my skills so that I may stay up to date with an ever changing society. So that I can use digital tools practically, I need to ensure I am using them often and am learning as I go.
Identify your present values and beliefs about ICT in the classroom. Keep it brief and focused.
ICT is a vital tool for all student to keep up to date with and explore new avenues of learning in this ever-evolving society we live in. I believe that ICT is a great tool but I also can at times worry that students are too addicted to the use of them and at times do not understand that they are to be used as tools, rather than for games.
Your approach to teaching and learning
I aim to become a ITD and HPE teacher and know that technology will be used when teaching graphics, woodwork, metal work and even in HPE. I will use a mixture of hands-on approaches as well as allowing students to be creative through digital tools.
Identify any challenges to your current values and beliefs as you enter this unit?
So that I can best teach these subjects, I need to have an understanding on how to use theses programs myself. In high school I used certain technology’s when learning Graphics and manual arts subjects, but these technologies are most likely outdated now as that were many years ago. Hence, I will need to familiarize myself with modern technology.
What experience do you have with ICT in the classroom?
I am familiar with iPads as I currently work in a primary school as a teacher aide and have seen many ways that teacher have used this in the classroom. It is expected that when I teach in high school that I will need to be familiar re with eh use of laptops
The Contemporary Learner
Who is the contemporary learner?
How will the
characteristics of our Gen Z learners depicted in the Meet Gen Z video define
their engagement in the traditional classroom snippet?
The students in this video are disengaged.
The teacher is not working collaboratively with the students. There is also no
involvement of the students in the discussion or any need for them to
participate. He is not using the current teaching standards (APST) (AITSL)
i.e., ‘Know your students and how they learn’. Gen Z live in a world where they
are constantly stimulated, meaning there is constantly more than one thing
going on. If Gen Z students were taught in the way this video displays, they
would not actively learn and would become bored very quickly, as seen in the
video.
Referring to the ideas presented by Willis
and Robinson, is this level of creativity in evidence in the schools
you have attended, both as a student, and as a preservice teacher? Furthermore,
is this level of creativity in evidence in your University units? As secondary
pre-service teaching students, you will experience a variety of approaches to
teaching, learning and course design in your discipline studies. Why were your
previous studies presented in that particular way? How could they have been
presented?
In my opinion, the level of creativity was
not as evident when I was at school compared with how I see it today as a
pre-service teacher. Creativity has many more avenues today for students to
explore and learn from. The Professional Teaching Standards have since changed
and evolved and become more related to students as the core structure to how
planning for teaching and learning is based on.
What do you think the implications are
of a curriculum that is linear, progressive, aimed at a single learning outcome
for the development of both individuals and the society we live in?
When only aiming for a single learning
outcome, many students who learn differently, are thus left out. When allowing
students to show their knowledge in varying ways and through different
measures, they can feel success and can be included when assessing
capabilities. The society we live in today allows citizens to work in many
capacities and thrive in creativity. To consider this, educational settings
must prepare them for this and allow flexible learning.
How can ICTs help you in the development
of a professional learning network? How are you feeling about this?
One example of networking professionally,
is right now as a pre-service teacher, connecting with other pre-service
teachers. As a ‘distant/online’ student, my main form of contact is through
online forms and interreacting with recorded lectures and tutorial meetings. So
far, I have already connected with many students who are in the same learning
journey as me and have received and given advice that has been beneficial
towards my Teaching Degree.
Pedagogical Principles
What are the Pedagogical Principles (defined in the Learning Materials)?
The Pedagogical Principals are defined
as:
1. Facilitating deep knowledge through higher order thinking
2. Facilitating collaborative learning in which conversations are important
3. Supporting students in knowing how they learn best
4. Planning learning that is problem-based, and situated in real life contexts
5. Is relevant to students, and connects to their background knowledge
6. Supports learning that is owned, controlled and managed by students themselves
7. Is socially supportive, engaging, and values cultural knowledges
8. Is supportive of the development of active citizenship, and strong group identity.
Retrieved from: A Guide to Productive Pedagogies (unimelb.edu.au)
What do the Pedagogical Principles mean
to you in common language?
Pedagogical principles mean that as I
continue my degree I need to work out the best teaching pedagogies that suit
me, in order to have a planned approach to teach the students authentically.
This will support student learning and my individual teaching approach. It will
help me form relationships with students where I am confident in my practice.
Consider whether the Pedagogical
Principles make sense to you in terms of your own experience in learning that
has a) been pedagogically sound, and b) been pedagogically woeful?
Throughout my high school, my job as a
Teacher Aid and as a university student I have experienced pedagogical
principles being implemented successfully as well as ineffectively. As a school student, I remember feeling bored
and disengaged through a few of my high school subjects. I feel this was
because of the way teacher was relaying the information and not making it easy
to understand or comprehend, particularly for a student like myself where I
needed extra time to process new information. However, I found ITD and HPE to
be subjects that I enjoyed as the pedagogical principles were sound.
Can you recognise these pedagogies in
the experiences you have identified in the sound category? Elaborate.
Throughout high school, I found that my ITD
and HPE subjects were definitely in the sound category. Firstly, because my
teachers where enthusiastic and made what we were learning interesting.
Secondly, because it was engaging. Finally, because it was relatable to real
life.
Beyond this, can you identify the links
between Judy Willis' knowledge of the brain and learning, Sir Ken Robinson's
perspective on creativity, the needs of your contemporary learners and these
pedagogical principles?
I can identify links between Judy Willis'
Knowledge of the brain and the messages she gives. Her pedagogical ways of
Teaching were aimed at reducing students' boredom during class and encouraging
their engagement. These are similar to Sir Ken Robinson, as he advocates
creativeness and encourages outside the box thinking. These ideas are
inspirational, for they evolve students' higher order thinking. Thus, the
students become more creative and critical thinkers, more engaged and
ultimately become contemporary learners reaching their full potential.
Why is it important to engage social
interaction and prior knowledge, and plan for individualised and socially
supportive, valued learning?
It is important to engage students in
social interaction and use their prior knowledge to develop an understanding of
what student already know and how they can incorporate that into what they are
learning about. Planning for social and individualised interactions, ensures
students can apply every-day knowledge and considerations, making the learning
more approachable and attainable.
Reflect on your experiences of pedagogy
as a learner. How many of these pedagogies are you familiar with?
I am reflecting on my post-school cabinet
making apprenticeship. This is where I remember our teacher using Pedagogy
Principle (2) 'Facilitating collaborative learning in which conversations are
important', when allowing students to work together when using timber. (4)
'Planning learning that is problem-based, and situated in real life
contexts' and (8) 'Is supportive of the development of active citizenship, and
strong group identity' were also seen when we were put in groups to work
collaboratively and come up with solutions to make a timber based product that
would be useful and efficient in real life scenarios.
Bloom's Taxonomy - Higher Order Thinking
Reflecting on higher order thinking
Secondary discipline areas are often content-laden. Use Robyn Collins Curriculum and Leadership as a foundation, and consider the Australian Curriculum in your selected junior discipline area. Identify the process/research/inquiry skills that are required. They are skills that, according to Collins, are best developed through application to real-life contexts. Use the Aims, rationale and structure of the curriculum to uncover the global approaches of importance, as well as the content.
Collins states "the extent to which higher-order thinking skills are taught and assessed continues to be an area of debate, with many teachers and employers expressing concern that young people ‘cannot think’". This is important note in all subjects, particularly in HPE, one of my junior disciplinary Key Learning Areas(KLA). There are many assumptions that HPE is easy and does not involve much thinking as it is 'just running around and playing games'. However, just as in other in KLAs, critical thinking is required. For example, in years 7 and 8, students are to "Evaluate strategies to manage personal, physical and social changes that occur as they grow older (ACPPS071) (ACARA)". The verb 'evaluate' is one of the Bloom's Taxonomy forms of higher-order thinking. This curriculum descriptor aims to encourage students to evaluate changes that relate to themselves and others in society.
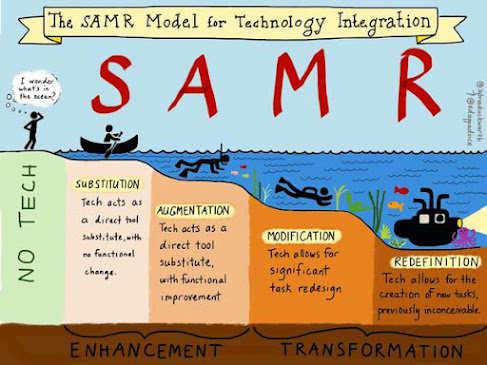
SAMR Drawing it all together
Write a reflection that draws together Blooms Taxonomy, your understanding of ICT pedagogy and the SAMR model as it relates to your teaching context.
Rather than think about what you have experienced in schools, try to take an aspirational position on this reflection. Examine not what currently exists, but what is possible.
This will become the foundation of your own pedagogical framework which will later be mapped against a learning design.
When reflecting on Blooms Taxonomy, ICT pedagogies and the SAMR Model, it can be noted that the SAMR Model and Bloom's Taxonomy are similar frameworks, showing progressions in levels of learning and tools required to progress. As mentioned previously, when students are evaluating 'strategies to manage personal, physical and social changes' (ACPPS071), they can use technological tools in varying ways, either substituting, augmenting, modifying and redefining tasks. When given this task, at first the task can be set out in the first stage of the Gradual Release of Responsibility Model (GRRM), where the teacher is using technology by substituting and augmenting. Then when students apply critical thinking, they can modify and redefine using technological tools, the 'You Do' stage in GRRM. Technology pedagogies need to demonstrate understanding of the progressions of the mentioned frameworks, to ensure students can achieve their potential and are not given limitations.
Legal, safe and ethical ICT practice
Legal, safe and ethical practice and what it means for you
What are the dimensions of legal, safe and ethical practice outlined in the Australian Curriculum: ICT as a General Capability?
This information is taken from ACARA:
This element involves students developing an understanding of how social and ethical protocols and practices are applied when using ICT.
Students apply appropriate practices to recognise the intellectual property for digital information of themselves and others. They use appropriate practices for the physical and logical storage and security of digital information, and apply appropriate protocols when using ICT to safely create, communicate or share information. Students gain an understanding of the benefits and consequences of the use of ICT by individuals, groups and communities and the impact of the use of ICT on the fabric of society. In developing and acting with ICT capability, students:
- recognise intellectual property
- apply digital information security practices
- apply personal security protocols
- identify the impacts of ICT in society.
What will you need to consider in your curriculum learning areas?
When considering legal, safe and ethical practice using ICT, here are some examples that relate to Industrial Technology and Design (ITD) and Health and Physical Education (HPE):
ITD:
- intellectual property when creating designs for products in timber, metal and graphics
- security protocols when saving their work and designs
- apply digital information security practices when searching online for inspiration
HPE:
- identifying the impacts of ICT in society when analysing Health curriculum concepts
- apply personal security protocols when answering personal information
Reflection 1 Web Spaces
My experience with Blogger and Google Sites so far.
When initially engaging with this unit, admittedly, I felt overwhelmed and unsure as I have not had much experience using online sites, other than consuming social media. However, I have learnt a lot about Blogger through the use of uploading my blogs and spending time navigating the settings. As a student I have learnt through my own attempts and trial and error. I have found Blogger straight forward, at times, to navigate and work out. I have seen the tools it provides and can see how this could be used in a classroom with my future students. Students can create their own templates and styles of blog layouts. They can include images and links, just as I have. |
| Original layout |
 |
Legal, safe and ethical protocols
Suggestions
One example of how online spaces could be used when teaching ITD is by getting students to create a webpage advertising a product they have made or intend to. When considering the SAMR Model for this activity, the below outlines different stages of the model:
Instructional design/SAMR Model/
They are many benefits to using online sites in the classroom but careful consideration is required, to ensure students are not just consumers but are using higher-order thinking and are critically aware of the uses of ICT for educational tools.
This video demonstrates what future classrooms may look like and are already becoming.
What Will Schools Look Like in the Future? - YouTube
Freethink. (2016, December, 20). What will Schools Look Like in the Future? [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JZlgYiXzu58
Reflection 2 Digital Media

Digital Media in the classroom
The 21st century society is one full of digital media, with a wide range of ways to reach selected audiences, using images, video and audio. In every day occurrences, advertisements pop up continuously with great amounts of colour, appeal and things to be desired. Imagery and media cause a great influence on consumers and cleverly target relating audiences.
In the modern classroom, the use of digital media can help engage students, just as the use of Bitmoji and other digital media was intended within my previous blog post, to engage readers like yourself. Digital media can be used as a visual tool to explain examples that would otherwise be left to the imagination. This provide a focus point for what the intended focus is. One central idea can be shown through multiple representations e.g. YouTube videos, Ted Talk videos, infographics, pictures of scenarios and many more. Such creative tools allow for a visual representation that can demonstrate imagination, creativity, explanation and examples of ideas. by sharing digital media resources, others can be inspired, supported and can use digital media to further explain ideas and concepts.
Digital media can be incredibly flexible when created personally. However, when using pre-made resources, there are limitations to customisations. For example, when downloaded, YouTube videos can be adjusted but there must be recognition of the original creator, images can be altered but must also acknowledge original creator. Thus, for full customisation and tailored needs, one must create digital media resources from scratch.
When considering levels of difficulty, as with any tool, the more experience leads to more chances of success and less difficult requirements. For example, if a user has prior experience using PowerPoint, then creating infographics with this would be easier and straight forward to navigate. However, using a program like Canva may cause more difficult if the user has not previously used this or any similar online sites.
When creating digital artefacts, there are a plethora of available technologies that allow creativity and serve as useful tools and templates, some include, Powerpoint, Kahoot, iMovie, YouTube, Podcasts, Canva and Photoshop.
It is important to note some of these programs require subscriptions or payment plans.
(I created this imagery using PowerPoint)
Legal, safe and ethical protocols
Legal, safe and ethical protocols should be considered when creating digital media. Students need to understand what it means to have ownership of own creations and the need for watermarks when sharing online. They need to understand copyright and the importance of acknowledging use of premade sources. It is not ethical to copy other ideas and claim as own. Students need to know that what they post online, must be cybersafe and that everything has a digital footprint, which can be traced back to the students if they do not follow correct steps. Students need to ensure they are following safe protocols, for the students who are experiencing any cyber bulling to Block, Report and Support others who have or are experiencing similar experience.
Analyse the impact of effort, space, time, objects and people when composing and performing movement sequences (ACPMP103 - Scootle)
Substitution: students find images (through books or Google) of Soccer game drills and explore differences
References:
ACARA. (n.d.) Australian Curriculum: Health and Physical Education. Australian Curriculum https://www.australiancurriculum.edu.au/f-10-curriculum/health-and-physical-education
Queensland Government. (2022). Block, Report, Support. Department of Education. https://behaviour.education.qld.gov.au/supporting-student-behaviour/bullying-and-cyberbullying/block-report-support
Presentations Reflection 3
When considering applications for students and teachers to use for presentations, there are many out
there, one in particular is Prezi. Prezi can be used in all classrooms as it is an online source and does not require payment, as opposed to PowerPoint, which many students require a Microsoft Office account. Prezi allows creativity in flexible ways, rather than linear forms in the way of PowerPoint slides.It would not be expected that high school students would struggle using this presentation platform as adolescents are quite technologically advanced and could navigate the site quite easily. Students can also access their Prezi from home, making it more accessible outside of school hours. This gives students responsibility to choose how much effort they would like to put in, using their own time.
Teachers and students can both benefit from the use of this
program, as teachers can present a multitude of topics and students can
source and select the ones that they would either like to look at or complete
first. Prezi can be more interactive than PowerPoint as students have a lot more templates to choose from which can make their
presentation more unique and engaging.
Prezi can be created by making an online account. The basic version is free for 5 presentations. unlike with Power Point where you need a Microsoft office login and need to download the software onto the computer. Prezi is a good alternative to PowerPoint because you can send a link as opposed to a file, which means it is more accessible, particularly for students who don’t have PowerPoint installed or access to the same device each time. Alternatively, PowerPoint can be shared as a PDF but still takes up storage space.
When marking student work PowerPoint would be easier for teachers as it is not as
complicated or hard to navigate through as Prezi can be.
When using Prezi, it was not originally intended to make comparisons with PowerPoint. However, while using the program I reflected on other programs I have used and thus came up with these comparisons.
One way I would use Prezi in the classroom for my ITD students is for the students to go on to Prezi and create a map of their school and use that as the background of the presentation. Students could then have the presentation zoom into of all the safety concerns they would find around the school and how best to be aware of them and take safety precautions.
This video would be used within an introduction lesson.
When considering both PowerPoint and Prezi, I came up with these suggestions for ITD using SAMR
Substitution: Finding images to relate to safety instructions that is important when working in the workshop.Augmentation: Sequence instructions using the image and creating PowerPoint slides.
Modification: Students use Prezi to modify their PowerPoint project, making it more specific, unique and engaging.
Redefinition: Students make a screen recording of their Prezi (Safety around the school) and record their voice over the top of their presentation.
Legal, safe and ethical protocols
Students using Prezi need to be mindful of their privacy settings. They need to consider if it is accessible for
students and teachers and not to public users. Students need to understand ethical uses of the program and consider what is appropriate to present and to not steal ideas from others without referencing and considering copyright protocols.
Prezi. (n.d.). Prezi Dashboard. Prezi. https://prezi.com/dashboard/next/#/own/all
Vanderbilt University. (2022). Blooms Taxonomy. Centre for Teaching. https://cft.vanderbilt.edu/guides-sub-pages/blooms-taxonomy/


.png)